Integrated Condition Monitoring Solutions
for Wind Industry
Importance of Integrated Reliability Maintenance for WTG
 Reliability is important with all rotating machinery. In the case of wind turbines, if the turbine stops then it is no longer generating electricity, and therefore it is not earning revenue for the wind farm owner.
Reliability is important with all rotating machinery. In the case of wind turbines, if the turbine stops then it is no longer generating electricity, and therefore it is not earning revenue for the wind farm owner.Random wind speeds, and occasional high wind speeds affect the input-side of the gearbox. Changing load conditions on the generator affect the output-side of the gearbox. Wind turbines must potentially operate in corrosive sea air or in freezing conditions where icing becomes a problem.
Resonance of the blades and tower can contribute to reliability issues, and misalignment is a significant issue given the flexibility of the foundations.
Technologies for Reliability issue in WTG and the advantages of the same.
- Ultrasonic services–For YAW & PITCH bearings, Electrical & Mechanical Components
- Vibration Analysis-For Drive train components
- Laser Alignment- For drive train
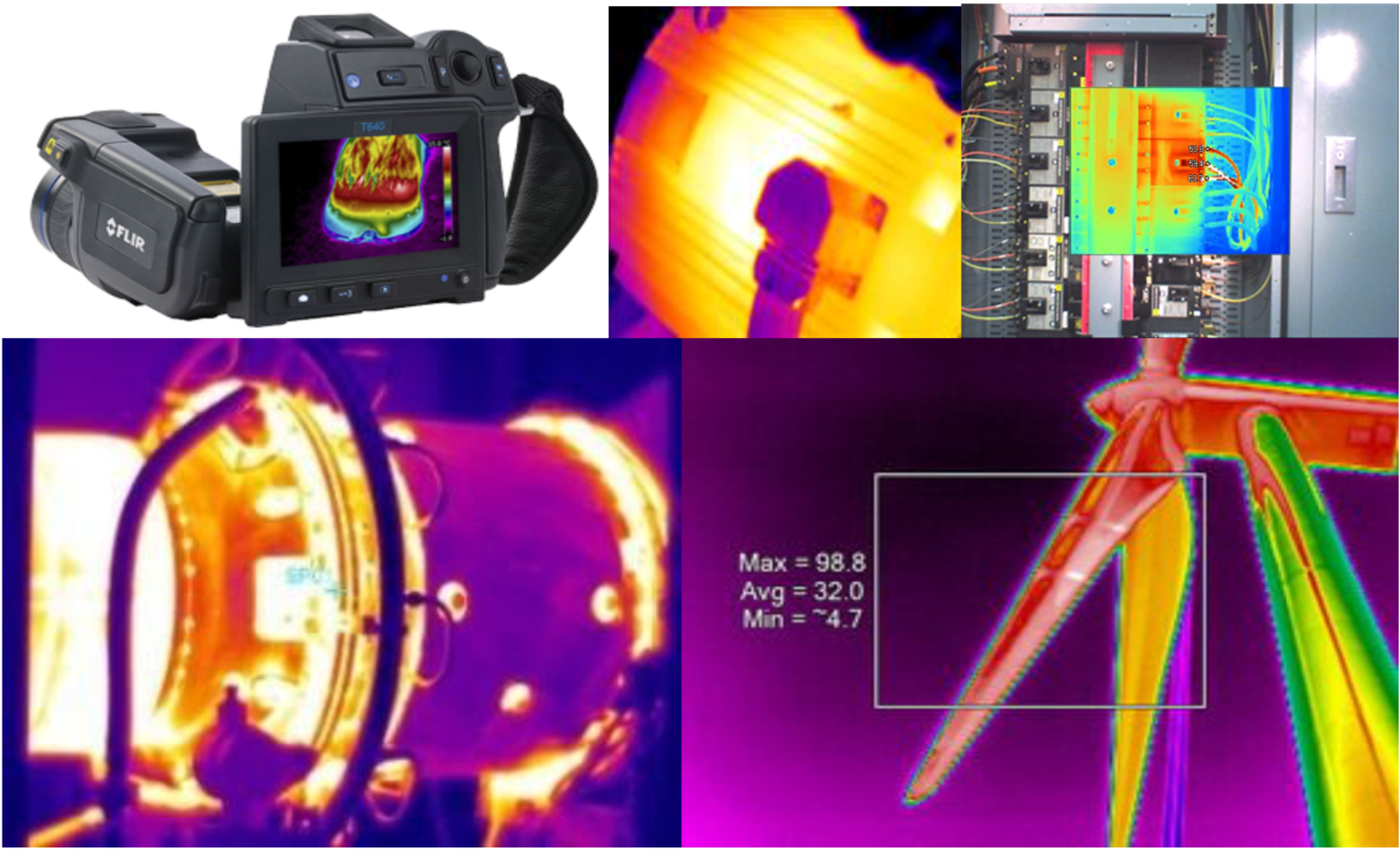
- Infrared Thermography-For Transformer, Generator, Electrical panels
- Oil Analysis - For Transformer
- Lube Oil Analysis-For Gearbox
- Grease Analysis-For Main Bearing & Generator bearings
- Ferrography-For Gearboxes machine condition
- Non Destructive Testing-For Casted &Forged components.
- Endoscopy Inspection - For Gearbox & Main Bearing
Ultrasound Inspection - Technology being used only by MVS ACMEI
Ultrasound instrument will provide the necessary informations to the maintenance team about various electrical & mechanical symptom parameters & its condition.Typical Applications of Ultrasound
MECHANICAL INSPECTION:- Lack of Lubrication / Failure
- Beginning of Fatigue Failure
- Brinelling of Bearing Surfaces
- Slow speed/VFD
- Prevent Over Greasing
- Partial Discharge
- Corona
- Tracking
- Arcing
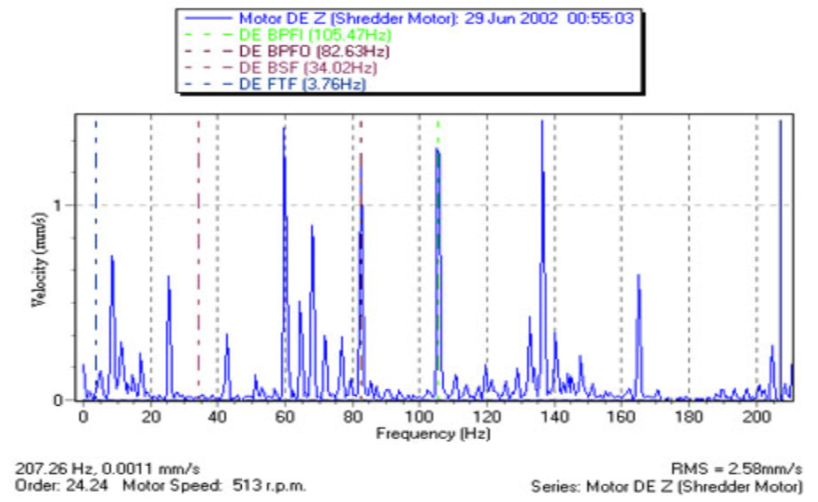
Vibration Analysis for Drive train
- Vibration can be a good indicator of the operating conditions of a range of mechanical components and structures and thus can support condition monitoring of important wind turbine components such as the rotor, drive train components and tower.
- Analysis of vibration signals in both the time and frequency domain can be used to identify incipient failure of these components.
- But the vibration sensor and analysis methods for tower and drive train components are different. For the Tower, Main Bearing, because the vibration frequency is quite low, a low frequency sensor (0–200 Hz) and an appropriate model based analysis method are used.
- For Drive train components Main bearing, Gearbox, Generator, a high frequency acceleration sensor (3–20 kHz) and fast Fourier transform (FFT), Cepstrum methods are used.
Shaft Alignment for Drive train
- Misalignment most affects the main bearings, gearbox and generator of wind turbines.
- The high-speed shaft between a gearbox and generator is a critical point of failure. Their misalignment a leading cause.
- Laser Alignment are a fast, easy, and accurate when used to align drive train components.
- A precision shaft alignment at install and periodic checks can help prevent drive train component failures, up-tower repairs, and catastrophic failures.
Thermography for Electrical & Mechanical components:
- Safety from hazardous accident.
- Non-contact method. Useful for far away targets.
- Can be done from safe distance.
- Night viewing possible.
- Done on live equipments.
- Time saving method.
- Pin points the thermal abnormality.
Boroscopic inspection of Gearbox & Main bearing:
- Boroscope inspections are visual inspections in places inaccessible to the human eye with the help of an optical device, the borescope.
- The borescope, also called videoscope or video boroscopy, a device is long and thin, flexible tube. Inside this tube is a telescopic system with many lenses, which provide a high image definition. It is also equipped with a powerful light source.
- The resulting image can be seen in the apparatus main lens, on a monitor, or recorded on a video recorder for later analysis.
Grease Analysis & Oil Analysis
- Oil analysis is well established as a routine tool to optimize maintenance activities, improve reliability and equipment life and prevent component failures.
- As part of a comprehensive Condition Based Maintenance program, lubricant analysis is an effective complement to other diagnostic technologies such as vibration analysis, infrared thermography, ultrasonic detection.
- However, when the component is grease lubricated rather than oil lubricated, the important lubricant analysis piece is often left out of the mix. The reasons for this include challenges in obtaining samples that can be trended, as well as the large sample volumes required for most current standardized tests for greases.
Vibration Data Collection and Analysis
We will be using the state of the art 4 channel data collector & the technical capabilities of the same as follows.CSI 2140-4 Channel Vibration Data collector


All possible machine fault symptoms of rotating/reciprocating machines can be identified as mentioned below:
- Unbalance (static, couple, quasi-static)
- Misalignment (angular, parallel, skew)
- Mechanical looseness, structural weakness, soft foot.
- Bend shaft, Rotor eccentricity.
- Resonance, best vibration.
- Mechanical rubbing
- Problems of belt driven machines
- Journal bearing defects.
- Antifriction bearing defects (inner race, outer race, cage, rolling elements).
- Hydrodynamic & Aerodynamic forces (blade of vane, flow turbulence, cavitations)
- Gear problems (tooth wear, tooth load, gear eccentricity, backlash, gear misalignment, and cracked or broken tooth.
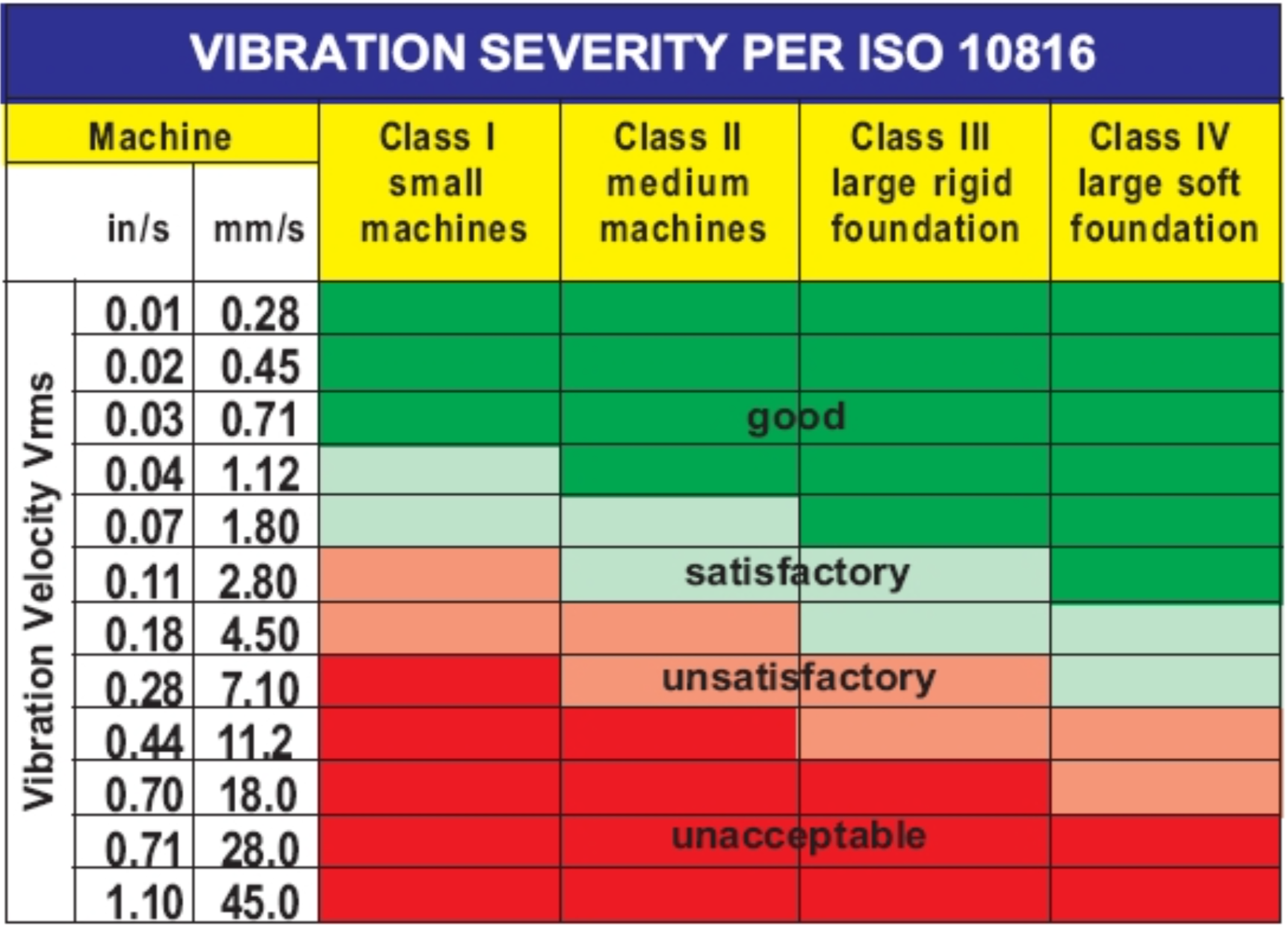
Vibration Severity Chart As per ISO 10816
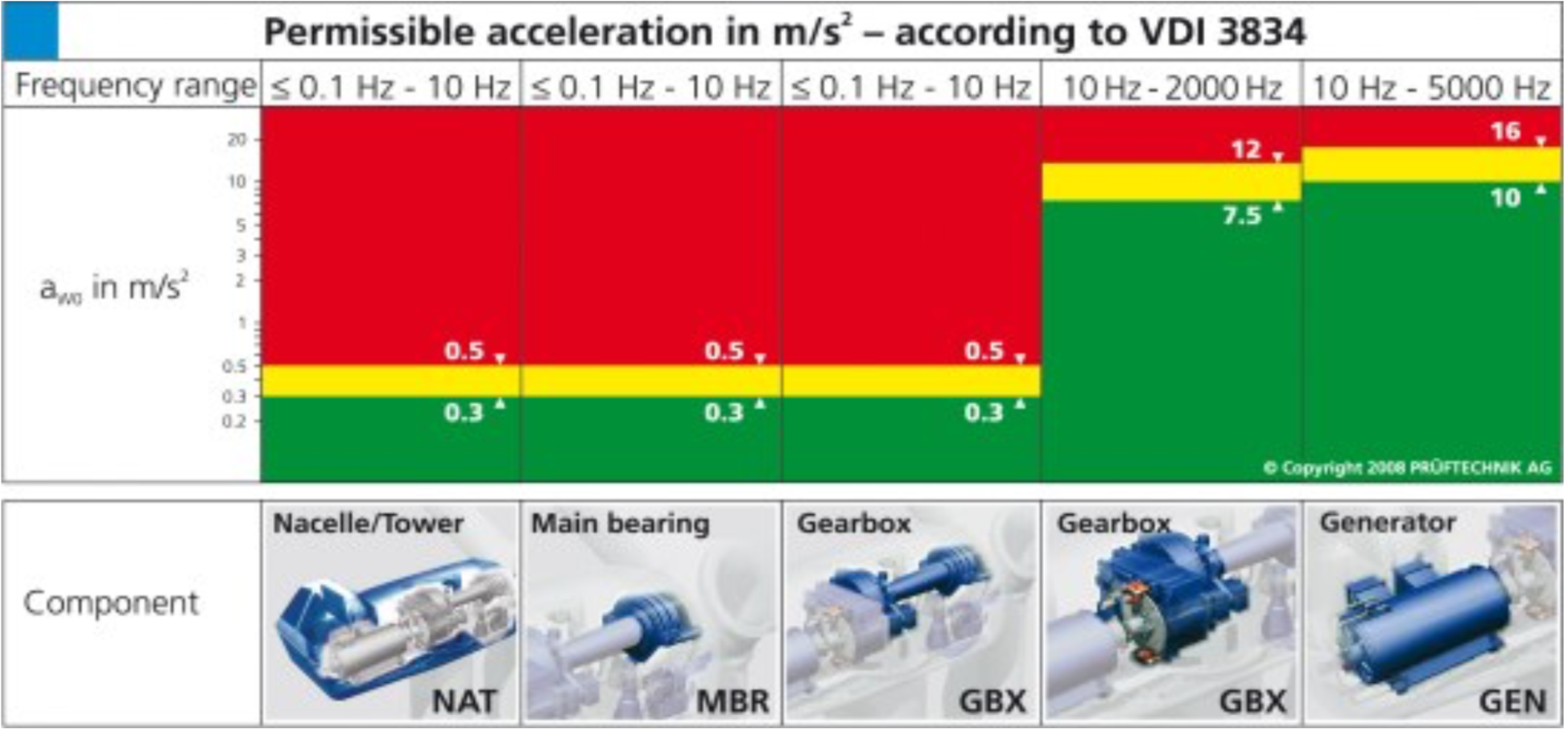
WIND TURBINE GENERATOR PERMISSIBLE VIBRATION STANDARDS
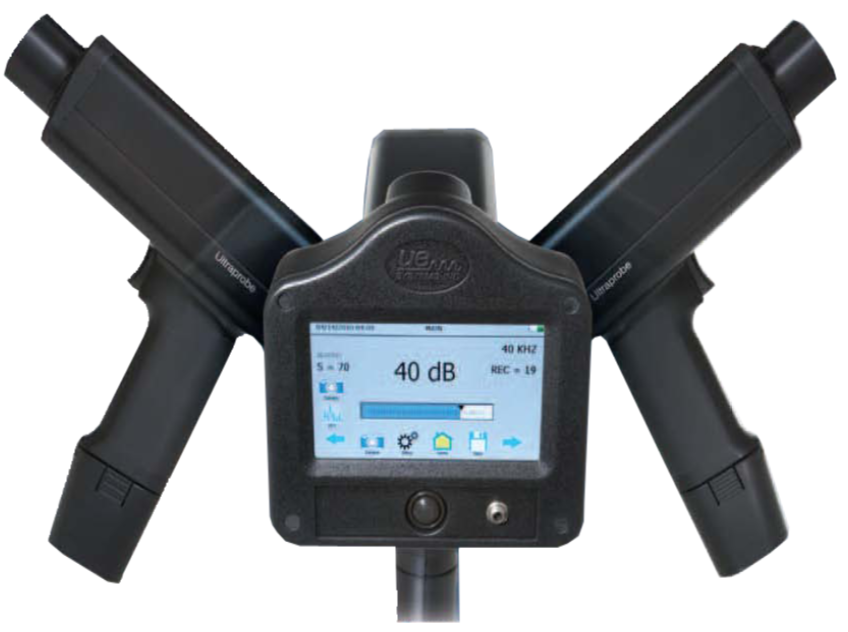
Ultrasonic Analysis for Slow Speed Bearing Analysis using UE 15000:
 Key Features:
Key Features:
- Ultraprobe 15,000 Touch Digital Ultrasonic Inspection System
- This advanced ultrasonic instrument can perform on- Board spectral analysis
- Record the sounds of test equipment,
- Measure and record temperature,
- Take photographs with flash,
- Store and manage data.
- The Ultraprobe 15,000 utilizes touch screen technology.
- This unique feature uses Icons to easily control and manoeuvre around any of the Ultraprobe's display screens.
- Touching the screen allows you to be able to view view decibel level, temperature, control sensitivity, change frequency, view an FFT and record sounds and images.
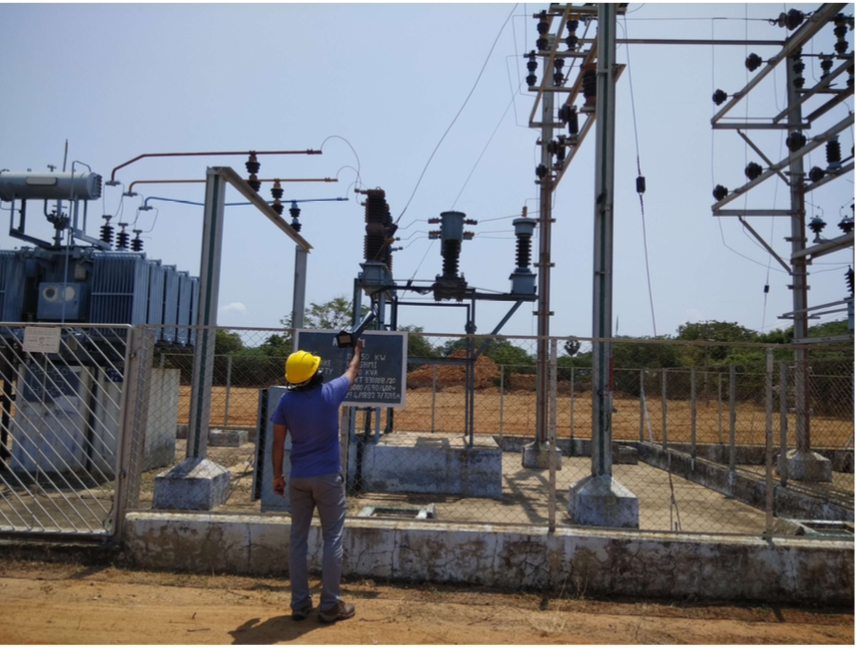 Ultra Probe 15000 Applications:
On-Board Analysis of Electrical Inspection.
Ultra Probe 15000 Applications:
On-Board Analysis of Electrical Inspection.For detection and analysis of these failure modes:
- Arcing
- Tracking
- Corona
 For use in these applications:
For use in these applications:
- Switch gear
- Transformers
- Insulators
- Relays
- Bus Brakes
 On Board Analysis of Mechanical Inspection/Trending
On Board Analysis of Mechanical Inspection/Trending
- Bearing Conditions
- Rubbing Conditions
- Cavitation
- Gears/Gear Boxes
- Pumps/Motors
- Lack of Lubrication / Over Lubrication
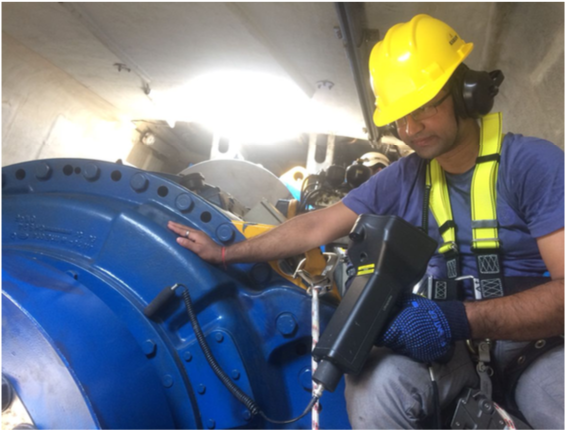
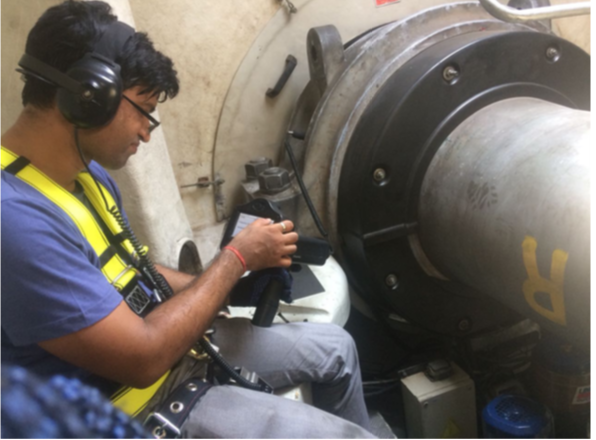
Laser Shaft Alignment of WTG Drive Train
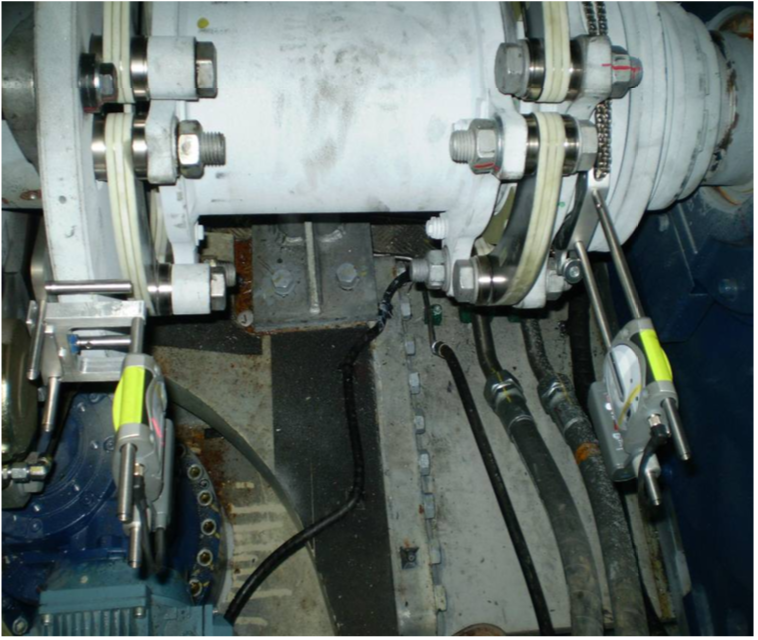
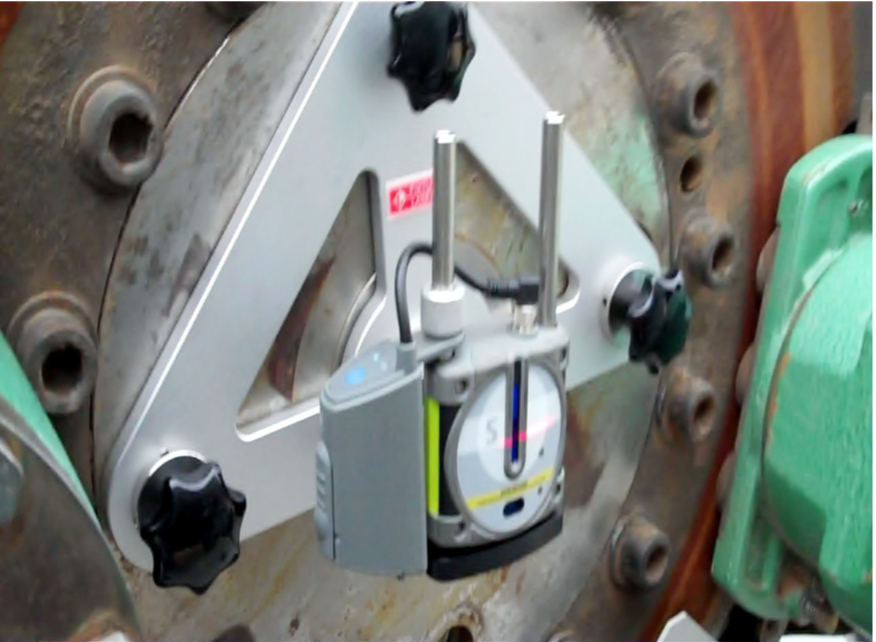
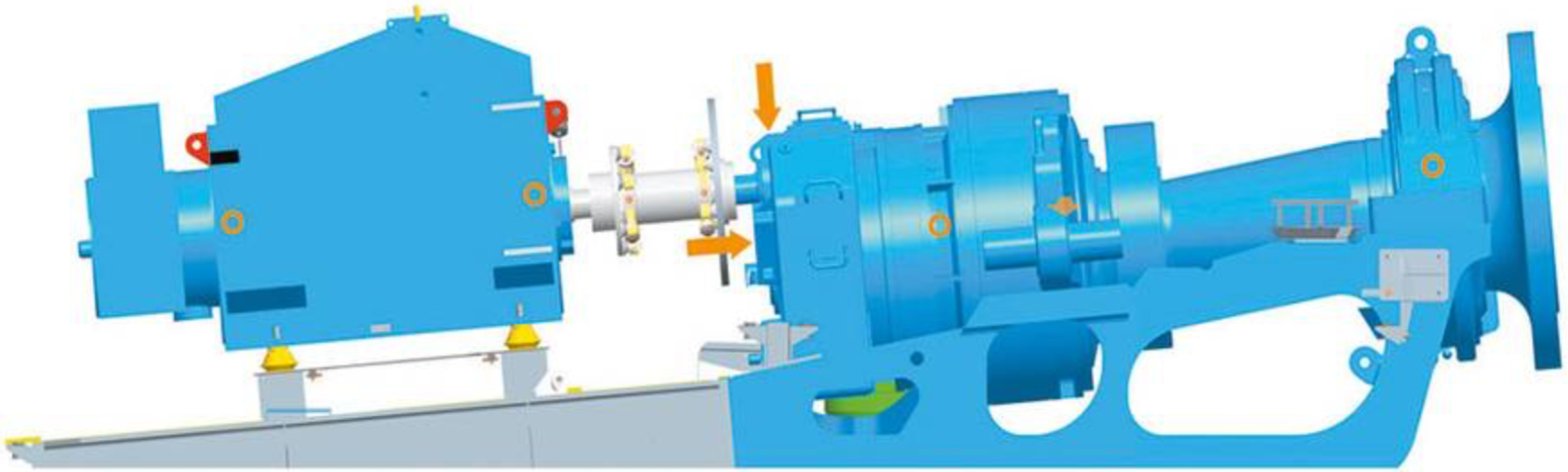



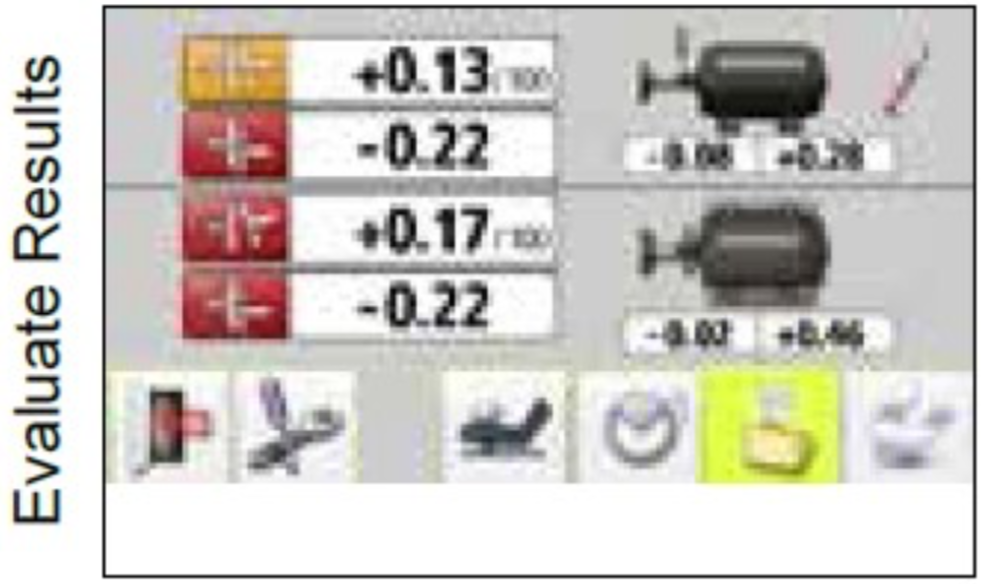
Benefits achieved by Laser Shaft Alignment are:
- Significant Power saving can be through accurate alignment.
- Protects the WTG assets and increases product quality as the vibrations are reduced to very low levels.
- Extends the machine availability as the mean time between failure increases.
- Increase in maintenance savings as spare parts consumption is reduced.
- Increase in time savings and Decrease in consumption of manpower for carrying out alignment..
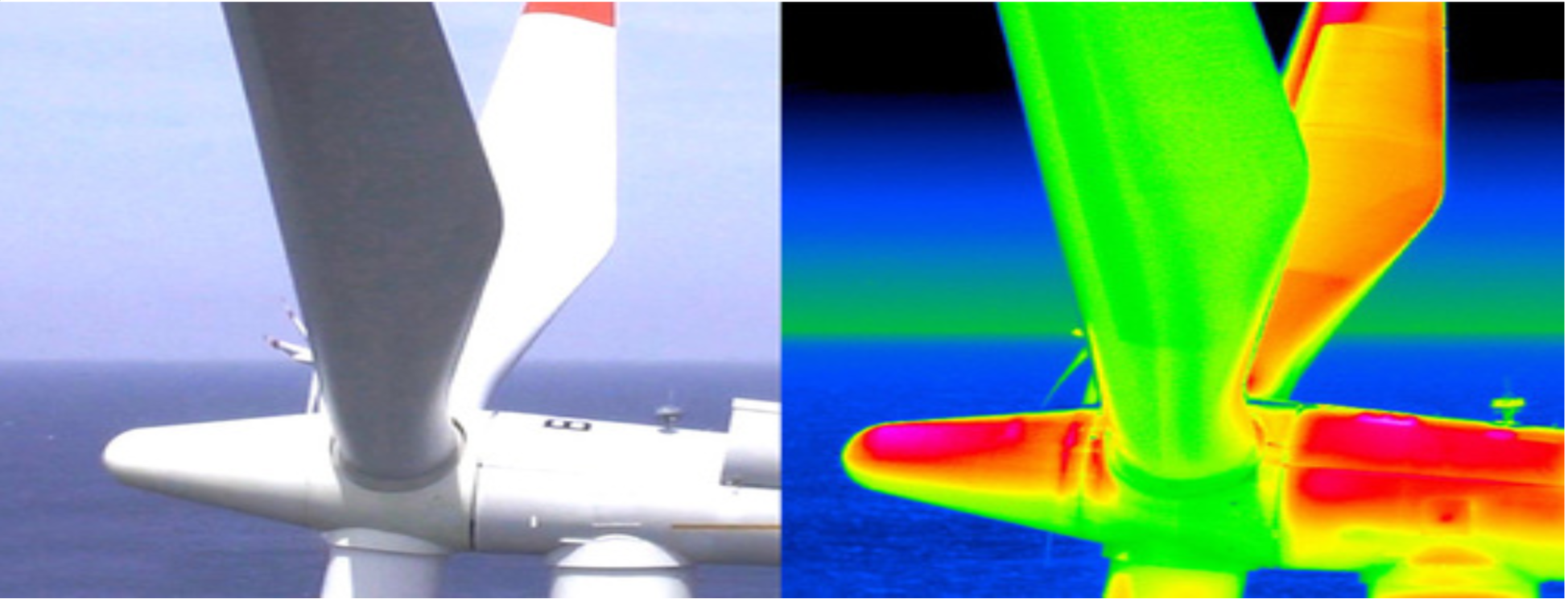
Infrared Thermography
The infrared camera evaluates and converts heat energy into meaningful temperatures. Components in various states of failure will emit more heat as a direct result of more energy dissipated into the component.This extra energy is caused by increased friction in mechanical devices, and higher resistance in electrical devices. For the following equipment thermography survey can be carried out.
| Application | Conditions Detected |
|---|---|
| Drives, Couplings, Gears, Shafts. | Overheated bearings or rollers, misalignment of shaft or coupling, lubrication failure uneven pressure. |
| Motors | Overheating of windings and bearings, blockages in cooling passages, friction, damping, material deformations, brush contact problems, rotors |
| Pumps/Fans/Radiators | Overheated bearings, high compressor discharges temperature, high oil temperature, and broken or defective valve. |
| Heavy Duty Equipment - Bearings, Brakes, Hydraulics | Overheating brakes, tires, bearings, pulleys, gears, gear or pulley misalignment, and blockages in hydraulics. |
| Mechanical Drive Components | High lube oil temperature, high bearing temperatures, faulty stop/control valve operation, uneven metal temperature, leaking shaft seals |
| Valves: Shutoff Valves, Relief valves | Leakage, Blockage. |
| Electrical inspections and electrical equipment | Unbalanced loads, Eddy current heating, Improperly sized fittings, Broken strands; Bad connections, breakers, fuses; Overloaded conditions, Motor Control Centre components, Distribution lines, Cable trays/conduits |